Introduction
kwui is a gui toolkit for creating graphical user interfaces. It works on Windows, and Android. kwui is released under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License, which allows for flexible licensing of client applications. kwui is inspired by rust-sciter, that use JavaScript and CSS to describe the UI, and Rust for business logic.
The kwui toolkit contains “widgets”: GUI components such as buttons, text input, or windows.
kwui depends the following libraries:
- Skia: Skia is a 2D graphics library with support for multiple output devices. More information available on the Skia website.
- Direct2D: Direct2D is a 2D graphics library for windows platform.
- QuickJS: QuickJS is a small and embeddable JavaScript engine.
kwui is divided into three parts:
-
kwui-rs: kwui-rs is the Rust binding to the C++ kwui-sys library.
- Provides simple and type-safe API.
- Integrate with cargo crates ecosystem.
-
kwui-sys: kwui-sys is written in C++. It inter-operates with underline operating system, render the user interface, and handle user input events. It's pretty complex, some features:
- Renderer:
Direct2DorSkia - Layout and style:
CSS - Scripting: builtin
JavaScriptengine withJSXextension support. - Data model:
React Hooksalike JavaScript functional components. - Platform-dependent resource system
- Renderer:
-
kwui-cli: kwui-cli is a command line tool.
- Create project template.
- Package application resources.
- Provide build assistance for Windows and Android target platform.
Quick Start
kwui supports Windows host only, targeting Windows and Android.
NOTE:
LinuxandOpenHarmony(OHOS)support in the future.
Installation
- Install the Rust development environments.
- Install kwui-cli tool.
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { cargo install kwui-cli }
First project
Let's create a hello world project my_proj:
- Create project from template.
# Creates a new Rust project 'my_proj' under current directory kwui new my_proj cd my_proj - Build and run.
cargo run
NOTE
kwui is using prebuilt library to accelerate the build process.
If your access to GitHub is difficult or slow, set the environment variable to use a mirror:
KWUI_BINARIES_URL=https://gitee.com/wanghoi/kwui-binaries/releases/download/{tag}/kwui-binaries-{key}.tar.gz KWUI_TEMPLATES_URL=https://gitee.com/wanghoi/kwui-binaries/releases/download/{tag}/kwui-templates-{key}.tar.gz
Porting to Android
- Prepare the Android development environment.
- Build the project for Android.
# Build 'app-debug.apk' kwui build apk - Install the resulting APK to your phone.
NOTE: only supports
arm64-v8aabi now.
Initializing kwui
Library initialization and main loop
Before using kwui, you need to initialize it with Application::new(); this connects to the operation system, sets up the locale and performs other initialization tasks. Application::quit() exits the application.
Like most GUI toolkits, kwui uses an event-driven programming model. When the application is doing nothing, kwui sits in the “main loop” and waits for input. If the user performs some action - say, a mouse click - then the main loop “wakes up” and delivers an event to kwui. kwui forwards the event to one or more elements in the gui Scene Tree.
User interface elements and input event callbacks are defined in JavaScript modules. After initialize kwui, you ScriptEngine::load_file(path) to load and run the root JavaScript entry script.
When elements receive an event, they frequently emit one or more “event callbacks”. Event callbacks calls into JavaScript function callback, that “something interesting happened”.
When your callbacks in JavaScript are invoked, you would typically take some action - for example, when an Open button is clicked you might update application states or perform some tasks with side effects. After a callback finishes, kwui will return to the main loop and await more user input.
Business code is written in Rust to perform network requests, and native operations. ScriptEngine is the bridge between Rust and JavaScript.
The main() function for a simple kwui application:
// src/main.rs use kwui::{Application, ScriptEngine}; pub fn main() { // initialize kwui let app = Application::new(); // set resource directory to local folder app.set_resource_root_dir(concat!( env!("CARGO_MANIFEST_DIR"), "/assets" )); // load 'assets/entry.js' ScriptEngine::load_file(":/entry.js"); // run event loop app.exec(); }
JavaScript in kwui
Entrypoint
assets/entry.js
kwui ScriptEngine load and run the JavaScript entry file: assets/entry.js. It shows a Dialog with parameters, such as dialog window width, height, and script module path of gui root component.
app.showDialog({
title: "Hello kwui",
width: 1280,
height: 720,
modulePath: "./hello.js"
});
assets/hello.js
assets/hello.js export the builder function, which invoked by kwui, to build root gui component and stylesheet on-demand.
// JSX syntax to define root component
function Hello(props, kids) {
return <div style="margin: 16px;">
<span id="hello">Hello kwui</span>
</div>;
}
// `css` is a builtin JavaScript template literal, to define CSS-in-JS
var hello_css = css`
#hello {
color: orangered;
}
`;
// root script module need to export the `builder` function
export function builder(moduleParams) {
return {
root: <Hello />,
stylesheet: hello_css,
}
}
Dialog
A dialog window is a top-level window mostly used for present graphics visuals and brief communications with the user.
app.showDialog()
let dialogId = app.showDialog({
title: "Hello kwui",
width: 1280,
height: 720,
modulePath: "./hello.js"
});
Create and show a new dialog window on Windows, replace root view content on Android.
app.closeDialog()
Close the specific dialog on Windows, on effects on Android.
app.closeDialog(this.dialogId);
Component Hooks
useState()
import { useState, useContext, createContext } from "Keact";
export function UseStateExample(props) {
let [n, setN] = useState(0);
return <button onclick={() => setN(n + 1)}>{`Click ${n} times`}</button>;
}
export function builder() {
return {
root: <UseStateExample></UseStateExample>,
stylesheet: css`
button { margin: 10px; padding: 4px; background-color: orange; }
button.dark { background-color: black; color: white; }
button:hover { background-color: orangered; }
`
};
}
useEffect()
import { useState, useEffect } from "Keact";
export function UseEffectExample(props) {
let [n, setN] = useState(0);
useEffect(() => {
console.log("useEffect setup, n:", n);
return () => console.log("useEffect cleanup, n:", n);
}, [n]);
return <button onclick={() => setN(n + 1)}>{`Click ${n} times`}</button>;
}
export function builder() {
return {
root: <UseEffectExample></UseEffectExample>,
stylesheet: css`
button { margin: 10px; padding: 4px; background-color: orange; }
button.dark { background-color: black; color: white; }
button:hover { background-color: orangered; }
`
}
}
useContext()
import { useState, useContext, createContext } from "Keact";
let [Theme, ThemeProvider] = createContext();
function Sub1(props, kids) {
return kids;
}
function Sub2(props, kids) {
let theme = useContext(Theme);
return <button class={theme}>Hello</button>
}
function ThemeExample() {
return <ThemeProvider value="dark">
<Sub1>
<Sub2></Sub2>
</Sub1>
</ThemeProvider>
}
export function builder() {
return { root: <ThemeExample /> };
}
Context properties
In component function, you can access creation context, from this object.
this.dialogId- the current dialog id where the Component is located.
Composite Pattern
Primitive Elements
Text
function ExampleTextComponent() {
return (<p id="text-container">
anonymous text span
<span id="simple-text">simple text span</span>
<span>{"escaped text: \u{f111}\u{f192}"}</span>
</p>);
}
var textStyle = css`
#text-container {
text-align: center;
}
#simple-text {
color: blue;
font-size: 24px;
}
Image
function ImageComponent() {
return <div id="img_a"></div>;
}
var imageStyle = css`
#id {
width: 32px;
height: 32px;
background-image: url(':/sample.png');
}
`;
Button
function ButtonComponent(props, kids) {
return <button onclick={() => console.log("clicked")}>Button</button>;
}
var buttonStyle = css`
button { margin: 10px; padding: 4px; background-color: orange; }
button:hover { background-color: orangered; }
`;
LineEdit
function LineEditComponent(props, kids) {
return <line_edit id="line-edit" value="abc"></line_edit>;
}
var buttonStyle = css`
#line-edit {
display: inline-block;
width: 200px;
height: 32px;
}`;
Rust and JavaScript Interop
Basic sample
use kwui::{Application, ScriptEngine, ScriptValue}; pub fn main() { let app = Application::new(); // set resource directory to local folder app.set_resource_root_dir(concat!( env!("CARGO_MANIFEST_DIR"), "/assets" )); // load 'assets/entry.js' ScriptEngine::load_file(":/entry.js"); // call JavaScript `function add(a, b) -> sum` from Rust let sum = ScriptEngine::call_global_function("script_add", &[ ScriptValue::new_int(1), ScriptValue::new_int(2), ]).to_int(); // export Rust function to JavaScript ScriptEngine::add_global_function("rust_add", rust_add); // run event loop app.exec(); } fn rust_add(a: i32, b: i32) -> i32 { a + b }
// call Rust function from JavaScript
console.log("sum:", rust_add(1, 2));
References
CSS in kwui
kwui has a builtin CSS parser and layout engine, implements a subset of CSS 2.2 Visual Formatting Model.
Supported CSS attributes
- position: static, relative, absolute
- display: none, inline, inline-block, block
- margin-*, border-*, padding-*
- width, height
- background-color, background-image
- border-radius
- color
- text-align, line-height, vertical-align
- line-height
Supported CSS selectors
- tag, class, id:
div {},.class1 {},#id - combinators:
div span {},div + span {},p, span {}
Style Scoped
Full, scoped and component-friendly CSS support for JSX, inspired by styled-jsx.
- Locally-scoped styles
- Co-location
- JavaScript variables in styles
function StyleComponent(props) {
return (<div class="style-root">
<style jsx>{`
div.style-root {
font-size: 24px;
}
span {
color: blue;
}
`}</style>
<span>blue text</span>
</div>);
}
kwui provide native support for scoped style. When your components render, static styles are cached for better performance. CSS reparse only occurs when you are using JavaScript variables in styles.
Note: scoped style feature was added in
v0.3.0.
Android Support
kwui has experimental android support now.
Requirements
kwui is targeting Android 11 (API level 30) or higher, and build for arm64-v8a target ABI now.
Android Emulator and ChromeOS are not supported yet.
Prepare Android development environment
- Install latest Android Studio
- Install latest Android SDK and NDK from Android Studio's SDKManager.
- Set the system environment variable, Example:
ANDROID_HOME=D:/projects/Android/Sdk
ANDROID_NDK_HOME=D:/projects/Android/Sdk/ndk/27.0.11718014
CARGO_TARGET_AARCH64_LINUX_ANDROID_LINKER=%ANDROID_NDK_HOME%/toolchains/llvm/prebuilt/windows-x86_64/bin/aarch64-linux-android30-clang.cmd
JAVA_HOME=D:/Program Files/Android/Android Studio/jbr
Build android apk
Enter the project directory, which is created by the kwui-cli tool.
cd test_proj
kwui build apk
Gallery
kwui has been used by many of author's internal projects, with many custom gui elements addons.
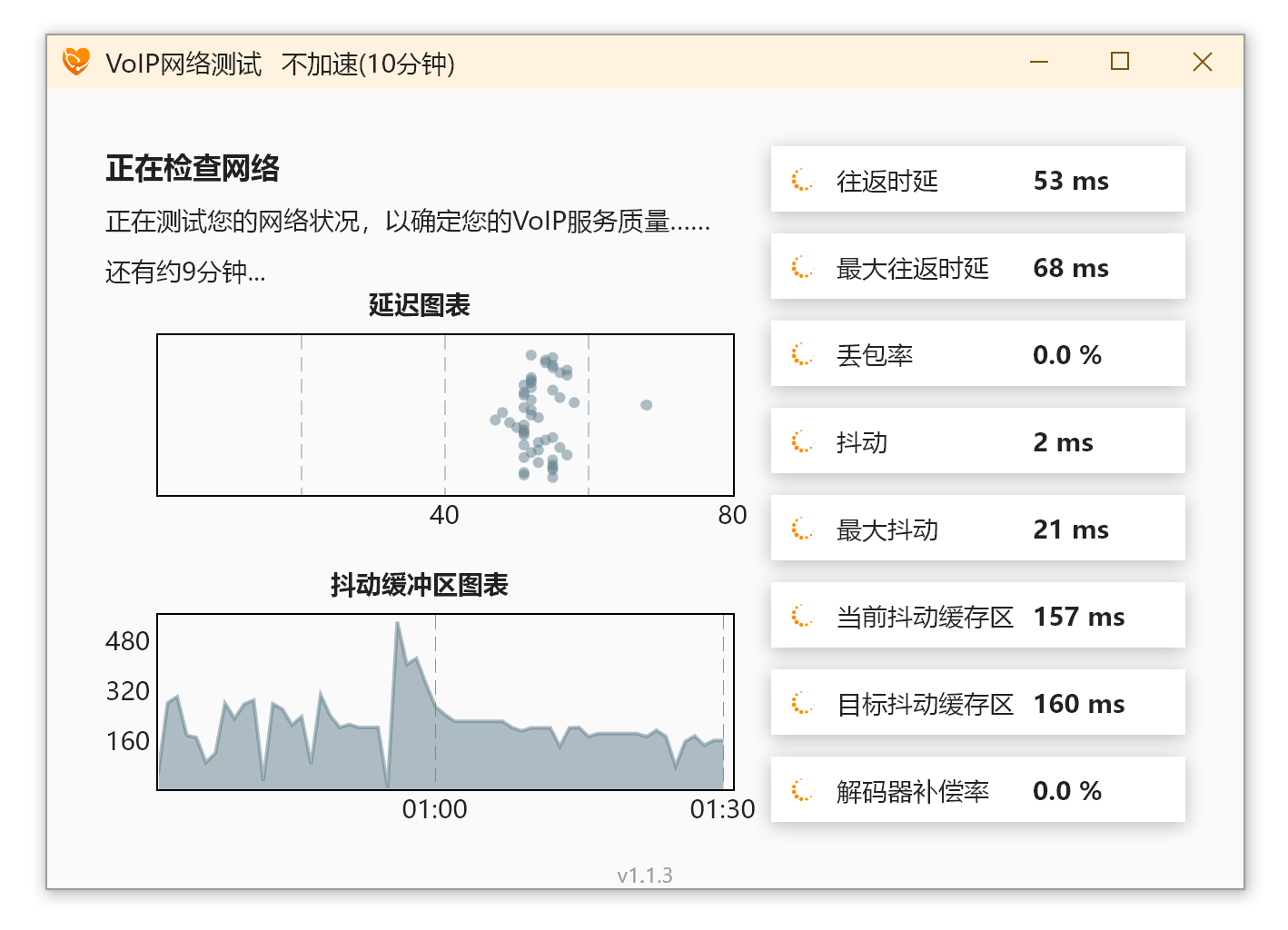
VoIP Test tool
Remote Desktop
Installer

Android examples
Common Questions
-
Why not Electron?
- Try new technology on mobile platforms quickly.
- Shorter development trial-and-error cycle.
-
What's the future plan?
- Add Rust api to create custom rendering gui elements.
- Better documentation.
- More test cases.
- Improve CSS support.
- OpenHarmony(OHOS) support.
QuickJS VM
QuickJS is a small and embeddable Javascript engine. It supports most of the ES2023 specification including modules, asynchronous generators, proxies and operator overloading.
kwui is using QuickJS to define user interface structure, and responds to user input events.
Features
- Small and easily embeddable stack based VM.
- Fast interpreter with very low startup time.
- Garbage collection using reference counting.
- Small built-in standard library.
- With simplified Rust API.
Compiling JavaScript
QuickJS compiles JavaScript to VM bytecode, with 3 passes:
- Parse JavaScript to generate initial bytecode.
- Resolve scoped variables to local or free variable references.
- Resolve and back patch jump offsets, peephole optimization.
JSValue Representation
JSValue is a Javascript value which can be a primitive type (such as Number, String, ...) or an Object.
kwui is compiling QuickJS with strict nan-boxing, for the purpose of cross-platform compatibility. JSValue is 64-bit on 32-bit and 64-bit platforms.
JSValue Format
QuickJS number is double-precision floating-point number. double type is 64-bit, comprised of 1 sign bit, 11 exponent bits and 52 mantissa bits.
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
seeeeeee|eeeemmmm|mmmmmmmm|mmmmmmmm|mmmmmmmm|mmmmmmmm|mmmmmmmm|mmmmmmmm
JSValue store non-NaN float with all bits binary reversed, therefore the first 12 bits are non-zero.
NaN numbers, and other primitive types, are represented by tag and value.
00000000|0000tttt|vvvvvvvv|vvvvvvvv|vvvvvvvv|vvvvvvvv|vvvvvvvv|vvvvvvvv
12-bits zero |tag| 48-bit placeholder for values: pointers, strings
| Primitive Type | tag | value |
|---|---|---|
| NaN number | 7 | 0 |
| -Inf number | 7 | 1 |
| +Inf number | 7 | 2 |
int | 1 | as-is |
false | 2 | 0 |
true | 2 | 1 |
null | 3 | 0 |
undefined | 4 | 0 |
exception | 6 | 0 |
object | 8 | JSObject* |
string | 11 | JSString* |
symbol | 12 | JSAtomStruct* |
Reference counted JSValue type (such as object, string, symbol), the most significant bit of tag is 1.
QuickJS Opcodes
ByteCode Compatibilities
The bytecode compatibilities of QuickJS VM, depends on macro defines.
We are compiling QuickJS with:
// #undef CONFIG_ATOMICS
// #undef CONFIG_BIGNUM
// #undef CONFIG_DEBUGGER
#define SHORT_OPCODES 1
- Atomics support disabled.
- Big number extension disabled.
- Debugger opcodes disabled.
- Extra short opcodes enabled.
ByteCode Module Format
After the JavaScript module file is compiled, the module's bytecode can be serialized, and loaded later.
Lexical-scope child functions are serialized recursively as parent function's constants.
Notation
- multi-bytes values are serialized in little endian order.
ATOM- interned string - when serialization, converted to zero started index.xB- length isxbytesLEB128- Little Endian Base 128 – length is a variable-length encoding format designed to store arbitrarily large integers in a small number of bytes. There are two variations: unsigned LEB128 and signed LEB128. These vary slightly, so a user program that wants to decode LEB128 values would explictly choose the appropriate unsigned or signed methods.STRING- string length, followed by utf-8 or utf1-16 string data
Compiled Module Specification
-
The compiled script module contains:
1B: version LEB128: number of atoms [STRING][STRING][STRING] : an array of atom strings MODULE: script module FUNCTION - module root function -
STRING
LEB128: for utf-8 string, `length << 1`, for utf-16 string, `(length << 2) + 1` [1B] or [2B]: utf-8 or utf-16 string data -
ATOM
LEB128: for intger atom, `(atom << 1) | 1`, for string atom, converted to `(first_atom + index) << 1` -
MODULE
1B: module tag, hex `0x0f` ATOM: module name LEB128: number of requested module entries [ATOM]: requested module name LEB128: number of exported module entries [LOCAL_EXPORT] or [INDIRECT_EXPORT]: local variable/function export or indirect export LEB128: number of star exported module entries [LEB128]: star exported module indexes LEB128: number of imported module entries [IMPORT]: imported modules -
FUNCTION
1B: function tag, hex `0x0e` 2B: flag, from lsb to msb: 1b: has_prototype 1b: has_simple_paramter_list 1b: is_derived_class_constructor 1b: need_home_object 2b: func_kind 1b: new_target_allowed 1b: super_call_allowed 1b: super_allowed 1b: arguments_allowed 1b: has_debug 1b: backtrace_barrier 4b: _unused_ 1B: js mode, 1: strict ATOM: function name LEB128: argument count LEB128: variable count LEB128: defined argument count LEB128: stack size LEB128: closure variable count LEB128: constant `JS_VALUE` pool count LEB128: bytecode length LEB128: `(arg_count + var_count)` [VAR_DEF]: `(arg_count + var_count)` variable definitions [CLOSURE_VAR]: `closure_var_count` closure variable definitions FUNCTION_BYTECODES - raw function bytecodes, atoms inside operands and converted to atom indices DEBUG_INFO - optional script debug information [JS_VALUE] - `cpool_count` - script constant values -
DEBUG_INFO
ATOM - script filename LEB128 - script start line number LEB128 - `pc2line_len` - size of the opcodes to line number table [1B] - `pc2line_buf` -
JS_VALUE
FUNCTION, STRING, OBJECT, or ARRAY
ByteCode References
Encoding
Each opcode is encoded by 1-byte opcode type, variable length operands. Each operand is little-endian encoded 1, 2, or 4-bytes length integer.
+--------+---------------------------+
| opcode | operand_1, operator2, ... |
+--------+---------------------------+
Typical operand types:
- index: index into the stack, or some array.
- label: jump label index or offset.
- value: literal value.
- atom: interned string.
Notation
a, b=>a + bindicates that theaddopcode takes two items off the stack (aandb) and places the sum of these two values on the stack. The leftmost item (a) is the top of the stack..=>aindicates that thepush_xxxopcode takes no stack item, and push a new item to the top of stack.- All stack descriptions elide subsequent items that may be on the stack. It can be assumed that unspecified stack elements do not influence the semantics of an operation, except when a stack overflow would result.
- The stack size is determined when compiling the script function, and all stack items are
JSValue. - Excluding the designated
invalidopcode, the QuickJS VM currently implements 245 opcodes, 66 of which are short opcodes indicating the number of operands (push_N,get_locN,put_locN,get_argN, ...). - Function arguments on stack are in reverse orders, the first argument is pushed to the stack first, therefore the last argument is on the top of the stack.
| Hex | Name | Operands | Stack |
|---|---|---|---|
| [notes] | [bytes]:[type] | top, bottom | |
| 00 | invalid | ||
| never emitted invalid opcode | |||
| 01 | push_i32 | 4: value | . => a |
| push the i32 value | |||
| 02 | push_const | 4: index | . => a |
| fetch value from the constant pool, push | |||
| 03 | fclosure | 4: index | . => a |
| must follow push_const, fetch function from the constant pool, bind var refs with current context, push the new closure | |||
| 04 | push_atom_value | 4: value | . => atom_a |
| push the atom value | |||
| 05 | private_symbol | 4: value | . =>
symbol_a |
| construct symbol from atom value, push | |||
| 06 | undefined | . =>
undefined |
|
push undefined constant value |
|||
| 07 | null | . => null |
|
push null constant value |
|||
| 08 | push_this | . => this |
|
| only used at the start of a function | |||
| 09 | push_false | . => false |
|
push false constant value |
|||
| 0A | push_true | . => true |
|
push true constant value |
|||
| 0B | object | . =>
object_a |
|
| push new empty object | |||
| 0C | special_object | 1: obj_type | . => object |
| only used at the start of a function, push new specially constructed object | |||
| 0D | rest | 2: value | . =>
array[args] |
push new array from current function's arguments, excluding
the first value args. |
|||
| 0E | drop | a => . |
|
| pop the stack | |||
| 0F | nip | a, b => a |
|
| remove the second value from the top | |||
| 10 | nip1 | a, b, c => a,
b |
|
| remove the third value from the top | |||
| 11 | dup | a => a, a |
|
| duplicate top value | |||
| 12 | dup1 | a, b => a,
b, b |
|
| duplicate and insert the second value | |||
| 13 | dup2 | a, b => a,
b, a, b |
|
| duplicate top two values | |||
| 14 | dup3 | a, b, c => a,
b, c, a, b, c |
|
| duplicate top three values | |||
| 15 | insert2 | a, b => a,
b, a |
|
| duplicate top value, insert at the third place | |||
| 16 | insert3 | a, b, c => a,
b, c, a |
|
| duplicate top value, insert at the fourth place | |||
| 17 | insert4 | a, b, c, d => a, b, c, d, a |
|
| duplicate top value, insert at the fifth place | |||
| 18 | perm3 | a, b, c => a,
c, b |
|
| swap the second and third value | |||
| 19 | perm4 | a, b, c, d => a, d, c, b |
|
| swap the second and fourth value | |||
| 1A | perm5 | a, b, c, d, e => a, e, c, d, b |
|
| swap the second and fifth value | |||
| 1B | swap | a, b => b,
a |
|
| swap the first and second value | |||
| 1C | swap2 | a, b, c, d => c, d, a, b |
|
| swap the first and third value, the second and fourth value | |||
| 1D | rot3l | a, b, c => c,
a, b |
|
| take off the third value, and push it to the top | |||
| 1E | rot3r | a, b, c => b,
c, a |
|
| take off the first value, and insert it to the third place | |||
| 1F | rot4l | a, b, c, d => d, a, b, c |
|
| take off the fourth value, and push it to the top | |||
| 20 | rot5l | a, b, c, d, e => e, a, b, c, d |
|
| take off the fifth value, and push it to the top | |||
| 21 | call_constructor | 2:argc | new_target, func_obj, args...
=> func_ret |
| take off the constructor target value, function object and its argments from stack, call object constructor, push constructor's return value to the stack | |||
| 22 | call | 2:argc | func_obj, args... => func_ret |
| take off the function object and its argments from stack, call function, push function's return value to the stack | |||
| 23 | tail_call | 2:argc | func_obj, args... => . |
take off the function object and its argments from stack,
call function, return the function's return value to the caller of JS_CallInternal() |
|||
| 24 | call_method | 2:argc | func_obj, this, args... => func_ret |
take off the function object, this
object, and its argments from stack, call method, push method's return value to the
stack |
|||
| 25 | tail_call_method | 2:argc | func_obj, this, args... => . |
take off the function object, this
object, and its argments from stack, call method, return the method's return value
to the caller of JS_CallInternal() |
|||
| 26 | array_from | 2:argc | args... =>
[args] |
| take off the function arguments from stack, push new array of arguments to the stack | |||
| 27 | apply | 2:magic | array[args], this, func_obj => func_ret |
| call function or method with array of arguments, magic value: 0 = normal apply, 1 = apply for constructor, 2 = Reflect.apply, push return value of function to the stack | |||
| 28 | return | func_ret =>
. |
|
take off the function return value from stack, and return
to the caller of JS_CallInternal() |
|||
| 29 | return_undef | . => . |
|
return undefined to the caller of JS_CallInternal() |
|||
| 2A | check_ctor_return | a => is_ctor_return,
a |
|
check a is undefined or object, derived class constructor must return an object or
undefined |
|||
| 2B | check_ctor | . => . |
|
check calling function's argument,
JSCallInternal(new_target), check new_target != undefined, class constructors must be invoked with 'new' |
|||
| 2C | check_brand | func, obj => func, obj |
|
check home object of func and obj has same brand, if failed, exception returned to the
caller to JS_CallInternal() |
|||
| 2D | add_brand | home_obj, obj => . |
|
add a brand property to object,
which points to the brand of home_obj |
|||
| 2E | return_async | . => . |
|
save VM execution state, return
undefined to the caller of JS_CallInternal() |
|||
| 2F | throw | except_obj => . |
|
| take off the exception object from stack, set it as VM's current_exception | |||
| 30 | throw_error | 4:atom, 1:type | . => . |
| throw an exception with type and error message atom | |||
| 31 | eval | 2:argc, 2:scope | eval_func, args... => func_ret |
take off the eval function object
and its argments from stack, call function, push function's return value to the
stack |
|||
| 32 | apply_eval | 2:scope | array[args], eval_func_obj => func_ret |
take off the eval function object
and its argments from stack, call function, push function's return value to the
stack |
|||
| 33 | regex | bytecode, pattern => regexp_obj |
|
| construct regular expression object from regexp bytecode and match pattern, push to the stack | |||
| 34 | get_super | obj =>
obj_super |
|
| get object's prototype type object, replace top stack value | |||
| 35 | import | specifier => module |
|
| dynamic module import | |||
| 36 | check_var | 4:atom | . =>
var_exists |
| check if a global variable exists | |||
| 37 | get_var_undef | 4:atom | . => a |
get global variable and push to the stack, push undefined if variable not exists |
|||
| 38 | get_var | 4:atom | . => a |
| get global variable and push to the stack, throw if variable not exists | |||
| 39 | put_var | 4:atom | a => . |
| set global variable from stack stop, normal variable write, if variable not exist, throw | |||
| 3A | put_var_init | 4:atom | a => . |
| set global variable from stack stop, if variable not exist, initialize lexical variable, | |||
| 3B | put_var_strict | 4:atom | a, strict => . |
set global variable from stack stop, if
strict is true, throw if variable not exists, else normal variable write |
|||
| 3C | get_ref_value | prop, this => this[prop] |
|
| get object's property | |||
| 3D | put_ref_value | a, prop, this => . |
|
set object's property, this[prop] = a,
if is_strict_mode(), throw if property not exists |
|||
| 3E | define_var | 4:atom, 1:flags | . => `` |
| define global variable | |||
| 3F | check_define_var | 4:atom, 1:flags | . => . |
| check global variable re-declaration, flags is 0, DEFINE_GLOBAL_LEX_VAR or DEFINE_GLOBAL_FUNC_VAR | |||
| 40 | define_func | 4:atom, 1:flags | func_obj =>
. |
| define global function | |||
| 41 | get_field | 4:atom | this => a |
pop this object, push this[prop] to the stack |
|||
| 42 | get_field2 | 4:atom | this => a,
this |
push this[prop] to the stack |
|||
| 43 | put_field | 4:atom | a, this =>
. |
set object property, this[prop] = a |
|||
| 44 | get_private_field | name, obj => a |
|
| get object private property | |||
| 45 | put_private_field | name, a, obj => . |
|
set object private property, obj[name] =
a |
|||
| 46 | define_private_field | a, name, obj => . |
|
set object private property, obj[name] =
a |
|||
| 47 | get_array_el | prop, this => a |
|
get array element, a = this[prop] |
|||
| 48 | get_array_el2 | prop, this => a, this |
|
get array element, a = this[prop] |
|||
| 49 | put_array_el | a, prop, this => . |
|
set array element, this[prop] = a |
|||
| 4A | get_super_value | prop, obj, this => a |
|
get object property, Reflect.get(obj,
prop, this), the value of this provided for the obj if a getter is encountered |
|||
| 4B | put_super_value | a, prop, obj, this => . |
|
set object property, Reflect.set(obj,
prop, a, this), the value of this provided for the obj if a setter is encountered |
|||
| 4C | define_field | 4:atom | a, this =>
this |
define object property, this[atom] = a |
|||
| 4D | set_name | 4:atom | obj => obj |
| set the name of object | |||
| 4E | set_name_computed | obj, name => obj, name |
|
| set the name of object | |||
| 4F | set_proto | proto, obj => obj |
|
| set the prototype of object | |||
| 50 | set_home_object | func_obj, home_obj => func_obj, home_obj |
|
| set the home object of function | |||
| 51 | define_array_el | a, prop, this => prop, this |
|
define array element, this[prop] = a |
|||
| 52 | append | enum_obj, pos, array => pos, array |
|
append to array, array[pos++] = a |
|||
| 53 | copy_data_properties | 1:mask | . => . |
copy properties value from source to target object, stack
offsets encoded in mask: 2 bits for target, 3 bits for
source, 2 bits for exclusionList |
|||
| 54 | define_method | 4:atom, 1:flags | a, obj =>
obj |
define object method, obj[atom] = a |
|||
| 55 | define_method_computed | 1:flags | a, atom, obj => obj |
define object method with computed method name, obj[atom] = a, must come after
define_method |
|||
| 56 | define_class | 4:atom, 1:flags | class_ctor, parent => proto, ctor |
| define a class object | |||
| 57 | define_class_computed | 4:atom, 1:flags | class_ctor, parent, name => proto, ctor |
| define a class object with computed class name | |||
| 58 | get_loc | 2:index | . => a |
push local variable var_buf[index]
to the stack |
|||
| 59 | put_loc | 2:index | a => . |
set local variable, var_buf[index] = a |
|||
| 5A | set_loc | 2:index | a => a |
set local variable, var_buf[index] = a |
|||
| 5B | get_arg | 2:index | . => a |
push function argument arg_buf[index]
to the stack |
|||
| 5C | put_arg | 2:index | a => . |
set function argument, arg_buf[index] =
a |
|||
| 5D | set_arg | 2:index | a => a |
set function argument, arg_buf[index] =
a |
|||
| 5E | get_var_ref | 2:index | . => a |
push variable reference var_refs[index]
to the stack |
|||
| 5F | put_var_ref | 2:index | a => . |
set variable reference, var_refs[index]
= a |
|||
| 60 | set_var_ref | 2:index | a => a |
set variable reference, var_refs[index]
= a |
|||
| 61 | set_loc_uninitialized | 2:index | . => . |
set local variable to JS_UNINITIALIZED
, var_buf[index] = uninitialized |
|||
| 62 | get_loc_check | 2:index | . => a |
get_loc with check for var_buf[index] != JS_UNINITIALIZED |
|||
| 63 | put_loc_check | 2:index | a => . |
put_loc with check for var_buf[index] != JS_UNINITIALIZED |
|||
| 64 | put_loc_check_init | 2:index | a => . |
put_loc with check for var_buf[index] == JS_UNINITIALIZED |
|||
| 65 | get_var_ref_check | 2:index | . => a |
get_var_ref with check for var_refs[index] != JS_UNINITIALIZED |
|||
| 66 | put_var_ref_check | 2:index | a => . |
put_var_ref with check for var_refs[index] != JS_UNINITIALIZED |
|||
| 67 | put_var_ref_check_init | 2:index | a => a |
put_var_ref with check for var_refs[index] == JS_UNINITIALIZED |
|||
| 68 | close_loc | 2:index | . => . |
| when leave scope, check to detach current stack frame's variable | |||
| 69 | if_false | 4:label | cond => . |
offset current instruction pointer if false, if (!cond) pc += label |
|||
| 6A | if_true | 4:label | cond => . |
offset current instruction pointer if true, if (cond) pc += label |
|||
| 6B | goto | 4:label | . => . |
offset current instruction pointer, pc
+= label |
|||
| 6C | catch | 4:label | . =>
catch_offset |
push a catch_offset JSValue to stack,
label is the offset from the start of current function's byte_code_buf |
|||
| 6D | gosub | 4:label | . =>
catch_offset |
push a catch_offset JSValue to stack,
label is the offset from the start of current function's byte_code_buf, and
offset current instruction pointer, pc += label, used to
execute the finally block |
|||
| 6E | ret | label => . |
|
set current instruction pointer, pc =
byte_code_buf + label, used to return from the finally block |
|||
| 6F | to_object | a => obj_a |
|
| convert top to stack to object | |||
| 70 | to_propkey | a =>
propkey_a |
|
| convert top to stack to property key, aka int, string, or symbol | |||
| 71 | to_propkey2 | a, obj => propkey_a,
obj |
|
test obj != undefined && obj !=
null, convert top to stack to property key, aka int, string, or symbol |
|||
| 72 | with_get_var | 4:atom, 4:label, 1:is_with | obj =>
new_obj |
replace stack top with obj[atom],
offset current instruction pointer, pc += label - 5 |
|||
| 73 | with_put_var | 4:atom, 4:label, 1:is_with | obj, a => . |
set object property, obj[atom] = a,
offset current instruction pointer, pc += label - 5 |
|||
| 74 | with_delete_var | 4:atom, 4:label, 1:is_with | obj =>
success |
delete object property, and push the delete status to
stack, offset current instruction pointer, pc += label - 5 |
|||
| 75 | with_make_ref | 4:atom, 4:label, 1:is_with | obj => atom,
obj |
push the property name to stack, offset current instruction
pointer, pc += label - 5 |
|||
| 76 | with_get_ref | 4:atom, 4:label, 1:is_with | obj => a,
obj |
get object property, a = obj[atom],
offset current instruction pointer, pc += label - 5 |
|||
| 77 | with_get_ref_undef | 4:atom, 4:label, 1:is_with | obj => a,
undefined |
get object property, a = obj[atom],
set old stack top to undefined, offset current instruction
pointer, pc += label - 5 |
|||
| 78 | make_loc_ref | 4:atom, 2:index | . => obj |
make a new object, and a new local variable reference, set object[atom] = get_var_ref(index) |
|||
| 79 | make_arg_ref | 4:atom, 2:index | . => obj |
make a new object, and a new function argument reference,
set object[atom] = get_var_ref(index) |
|||
| 7A | make_var_ref_ref | 4:atom, 2:index | . => obj |
make a new object, and a free variable reference, set object[atom] = var_refs[index] |
|||
| 7B | make_var_ref | 4:atom | . => atom,
global_obj |
| construct a reference to a global variable | |||
| 7C | for_in_start | obj =>
enum_obj |
|
construct for in iterator from
object |
|||
| 7D | for_of_start | obj => catch_offset,
method, enum_obj |
|
construct for of iterator from
object |
|||
| 7E | for_await_of_start | obj => catch_offset,
method, enum_obj |
|
construct for await of iterator
from object |
|||
| 7F | for_in_next | enum_obj => done,
value, enum_obj |
|
| iterator to the next value | |||
| 80 | for_of_next | 1:index | catch_offset, method, enum_obj
=> done, value, catch_offset, method, enum_obj |
| iterator to the next value | |||
| 81 | iterator_check_object | iter_ret =>
iter_ret |
|
| check iterator must return an object | |||
| 82 | iterator_get_value_done | iter_ret => done,
comp_val |
|
| check iterator must return an object, fetch the iterator complete value, and iterator done state | |||
| 83 | iterator_close | catch_offset, method, enum_obj
=> . |
|
| finalize iterator and cleanup | |||
| 84 | iterator_close_return | ret_val, ..., catch_offset, method,
enum_obj => catch_offset, method, enum_obj, ret_val |
|
| finalize iterator and cleanup | |||
| 85 | iterator_next | a, catch_offset, method, enum_obj
=> b, catch_offset, method, enum_obj |
|
call iterator next method, b =
iter_obj.method(a) |
|||
| 86 | iterator_call | 1:flags | a, catch_offset, method, enum_obj
=> ret_flag, b, catch_offset, method, enum_obj |
call iterator next method, b =
iter_obj.method(a), set ret_flag in accordance with flags |
|||
| 87 | initial_yield | . => . |
|
save VM execution state, return
undefined to the caller of JS_CallInternal() |
|||
| 88 | yield | . => . |
|
save VM execution state, return
FUNC_RET_YIELD to the caller of JS_CallInternal() |
|||
| 89 | yield_star | . => . |
|
save VM execution state, return
FUNC_RET_YIELD_STAR to the caller of JS_CallInternal() |
|||
| 8A | async_yield_star | . => . |
|
save VM execution state, return
FUNC_RET_YIELD_STAR to the caller of JS_CallInternal() |
|||
| 8B | await | . => . |
|
save VM execution state, return
FUNC_RET_AWAIT to the caller of JS_CallInternal() |
|||
| 8C | neg | a => -a |
|
| unary negative operator | |||
| 8D | plus | a => +a |
|
| unary plus operator | |||
| 8E | dec | a => a - 1 |
|
| unary decrement operator | |||
| 8F | inc | a => a + 1 |
|
| unary increment operator | |||
| 90 | post_dec | a => a - 1,
a |
|
push a - 1 to the stack |
|||
| 91 | post_inc | a => a + 1,
a |
|
push a + 1 to the stack |
|||
| 92 | dec_loc | 1:index | . => . |
decrement local variable, var_buf[index]
= var_buf[index] - 1 |
|||
| 93 | inc_loc | 1:index | . => . |
increment local variable, var_buf[index]
= var_buf[index] + 1 |
|||
| 94 | add_loc | 1:index | a => . |
add a to local variable, var_buf[index] = var_buf[index] + a |
|||
| 95 | not | a => ~a |
|
| binary not operator | |||
| 96 | lnot | a => !a |
|
| boolean not operator | |||
| 97 | typeof | a => typeof
a |
|
typeof operator |
|||
| 98 | delete | prop, obj => success |
|
| delete object property, return whether delete succeeds | |||
| 99 | delete_var | 4:atom | . =>
success |
| delete global object's property, return whether delete succeeds | |||
| 9A | mul | a, b => b *
a |
|
| multiply operator | |||
| 9B | div | a, b => b /
a |
|
| divide operator | |||
| 9C | mod | a, b => b %
a |
|
| modulate operator | |||
| 9D | add | a, b => b +
a |
|
| add operator | |||
| 9E | sub | a, b => b -
a |
|
| subtraction operator | |||
| 9F | pow | a, b => pow(b,
a) |
|
| power operator | |||
| A0 | shl | a, b => b
<< a |
|
| shift logical left operator | |||
| A1 | sar | a, b => b
>> a |
|
| shift arithmetic right operator | |||
| A2 | shr | a, b => b
>> a |
|
| shift logical right operator | |||
| A3 | lt | a, b => b
< a |
|
| less than compare | |||
| A4 | lte | a, b => b
<= a |
|
| less than or equal compare | |||
| A5 | gt | a, b => b
> a |
|
| greater compare | |||
| A6 | gte | a, b => b
>= a |
|
| greater or equal compare | |||
| A7 | instanceof | obj, cls => obj
instanceof cls |
|
| object is instanceof class | |||
| A8 | in | obj, prop => prop in obj |
|
| check object has property | |||
| A9 | eq | a, b => b
== a |
|
| equal compare | |||
| AA | neq | a, b => b
!= a |
|
| not equal compare | |||
| AB | strict_eq | a, b => b
=== a |
|
| strict equal compare | |||
| AC | strict_neq | a, b => b
!== a |
|
| not strict equal compare | |||
| AD | and | a, b => b
& a |
|
| binary and operator | |||
| AE | xor | a, b => b ^
a |
|
| binary xor operator | |||
| AF | or | a, b => b |
a |
|
| binary or operator | |||
| B0 | is_undefined_or_null | a =>
a_is_undefined_or_null |
|
check a === undefined || a === null |
|||
| SHORT OPCODES | |||
| short opcodes | |||
| B1 | nop | . => . |
|
| no-operation, VM will skip this opcode | |||
| B2 | push_minus1 | . => a |
|
short opcode, push a = -1 |
|||
| B3 | push_0 | . => a |
|
short opcode, push a = 0 |
|||
| B4 | push_1 | . => a |
|
short opcode, push a = 1 |
|||
| B5 | push_2 | . => a |
|
short opcode, push a = 2 |
|||
| B6 | push_3 | . => a |
|
short opcode, push a = 3 |
|||
| B7 | push_4 | . => a |
|
short opcode, push a = 4 |
|||
| B8 | push_5 | . => a |
|
short opcode, push a = 5 |
|||
| B9 | push_6 | . => a |
|
short opcode, push a = 6 |
|||
| BA | push_7 | . => a |
|
short opcode, push a = 7 |
|||
| BB | push_i8 | 1:value | . => a |
short opcode, push a = value |
|||
| BC | push_i16 | 2:value | . => a |
short opcode, push a = value |
|||
| BD | push_const8 | 1:index | . => a |
short opcode, push a = cpool[index] |
|||
| BE | fclosure8 | 1:index | . => a |
| short opcode, fetch function from the constant pool, bind var refs with current context, push the new closure | |||
| BF | push_empty_string | . => a |
|
| short opcode, push empty string | |||
| C0 | get_loc8 | 1:index | . => a |
short opcode, push local variable
var_buf[index] to the stack |
|||
| C1 | put_loc8 | 1:index | a => . |
short opcode, set local variable, var_buf[index]
= a |
|||
| C2 | set_loc8 | 1:index | a => a |
short opcode, set local variable, var_buf[index]
= a |
|||
| C3 | get_loc0 | . => a |
|
short opcode, push local variable
var_buf[0] to the stack |
|||
| C4 | get_loc1 | . => a |
|
short opcode, push local variable
var_buf[1] to the stack |
|||
| C5 | get_loc2 | . => a |
|
short opcode, push local variable
var_buf[2] to the stack |
|||
| C6 | get_loc3 | . => a |
|
short opcode, push local variable
var_buf[3] to the stack |
|||
| C7 | put_loc0 | a => . |
|
short opcode, set local variable, var_buf[0]
= a |
|||
| C8 | put_loc1 | a => . |
|
short opcode, set local variable, var_buf[1]
= a |
|||
| C9 | put_loc2 | a => . |
|
short opcode, set local variable, var_buf[2]
= a |
|||
| CA | put_loc3 | a => . |
|
short opcode, set local variable, var_buf[3]
= a |
|||
| CB | set_loc0 | a => a |
|
short opcode, set local variable, var_buf[0]
= a |
|||
| CC | set_loc1 | a => a |
|
short opcode, set local variable, var_buf[1]
= a |
|||
| CD | set_loc2 | a => a |
|
short opcode, set local variable, var_buf[2]
= a |
|||
| CE | set_loc3 | a => a |
|
short opcode, set local variable, var_buf[3]
= a |
|||
| CF | get_arg0 | . => a |
|
short opcode, push function argument
arg_buf[0] to the stack |
|||
| D0 | get_arg1 | . => a |
|
short opcode, push function argument
arg_buf[1] to the stack |
|||
| D1 | get_arg2 | . => a |
|
short opcode, push function argument
arg_buf[2] to the stack |
|||
| D2 | get_arg3 | . => a |
|
short opcode, push function argument
arg_buf[3] to the stack |
|||
| D3 | put_arg0 | a => . |
|
short opcode, set function argument, arg_buf[0]
= a |
|||
| D4 | put_arg1 | a => . |
|
short opcode, set function argument, arg_buf[1]
= a |
|||
| D5 | put_arg2 | a => . |
|
short opcode, set function argument, arg_buf[2]
= a |
|||
| D6 | put_arg3 | a => . |
|
short opcode, set function argument, arg_buf[3]
= a |
|||
| D7 | set_arg0 | a => a |
|
short opcode, set function argument, arg_buf[0]
= a |
|||
| D8 | set_arg1 | a => a |
|
short opcode, set function argument, arg_buf[1]
= a |
|||
| D9 | set_arg2 | a => a |
|
short opcode, set function argument, arg_buf[2]
= a |
|||
| DA | set_arg3 | a => a |
|
short opcode, set function argument, arg_buf[3]
= a |
|||
| DB | get_var_ref0 | . => a |
|
short opcode, push variable reference
var_refs[0] to the stack |
|||
| DC | get_var_ref1 | . => a |
|
short opcode, push variable reference
var_refs[1] to the stack |
|||
| DD | get_var_ref2 | . => a |
|
short opcode, push variable reference
var_refs[2] to the stack |
|||
| DE | get_var_ref3 | . => a |
|
short opcode, push variable reference
var_refs[3] to the stack |
|||
| DF | put_var_ref0 | a => . |
|
short opcode, set variable reference, var_refs[0]
= a |
|||
| E0 | put_var_ref1 | a => . |
|
short opcode, set variable reference, var_refs[1]
= a |
|||
| E1 | put_var_ref2 | a => . |
|
short opcode, set variable reference, var_refs[2]
= a |
|||
| E2 | put_var_ref3 | a => . |
|
short opcode, set variable reference, var_refs[3]
= a |
|||
| E3 | set_var_ref0 | a => a |
|
short opcode, set variable reference, var_refs[0]
= a |
|||
| E4 | set_var_ref1 | a => a |
|
short opcode, set variable reference, var_refs[1]
= a |
|||
| E5 | set_var_ref2 | a => a |
|
short opcode, set variable reference, var_refs[2]
= a |
|||
| E6 | set_var_ref3 | a => a |
|
short opcode, set variable reference, var_refs[3]
= a |
|||
| E7 | get_length | a =>
length(a) |
|
| short opcode, get length of stack top value | |||
| E8 | if_false8 | 1:label | cond => . |
short opcode, offset current instruction pointer if false, if (!cond) pc += label |
|||
| E9 | if_true8 | 1:label | cond => . |
short opcode, offset current instruction pointer if false, if (cond) pc += label |
|||
| EA | goto8 | 1:label | . => . |
short opcode, offset current instruction pointer, pc += label |
|||
| EB | goto16 | 2:label | . => . |
short opcode, offset current instruction pointer, pc += label |
|||
| EC | call0 | func_obj =>
func_ret |
|
short opcode, for call with argc
= 0 |
|||
| ED | call1 | func_obj, arg0 => func_ret |
|
short opcode, for call with argc
= 1 |
|||
| EE | call2 | func_obj, arg0, arg1 => func_ret |
|
short opcode, for call with argc
= 2 |
|||
| EF | call3 | func_obj, arg0, arg1, arg2 => func_ret |
|
short opcode, for call with argc
= 3 |
|||
| F0 | is_undefined | a => a ===
undefined |
|
short opcode, check a === undefined |
|||
| F1 | is_null | a => a ===
null |
|
short opcode, check a === undefined |
|||
| F2 | typeof_is_undefined | a => typeof
a === 'undefined' |
|
short opcode, check typeof a ===
'undefined' |
|||
| F3 | typeof_is_function | a => typeof
a === 'function' |
|
short opcode, check typeof a ===
'function' |
|||
| TEMPORARY OPCODES | |||
| temporary opcodes, removed later | |||
| B2 | enter_scope | 2:scope | . => . |
removed later in resolve_variables() |
|||
| B3 | leave_scope | 2:scope | . => . |
removed later in resolve_variables() |
|||
| B4 | label | 4:label | . => . |
removed later in resolve_labels() |
|||
| B5 | scope_get_var_undef | 4:var_name, 2:scope | . => . |
removed later in resolve_variables() |
|||
| B6 | scope_get_var | 4:var_name, 2:scope | . => . |
removed later in resolve_variables() |
|||
| B7 | scope_put_var | 4:var_name, 2:scope | . => . |
removed later in resolve_variables() |
|||
| B8 | scope_delete_var | 4:var_name, 2:scope | . => . |
removed later in resolve_variables() |
|||
| B9 | scope_make_ref | 4:var_name, 4:label, 2:scope | . => . |
removed later in resolve_variables() |
|||
| BA | scope_get_ref | 4:var_name, 2:scope | . => . |
removed later in resolve_variables() |
|||
| BB | scope_put_var_init | 4:var_name, 2:scope | . => . |
removed later in resolve_variables() |
|||
| BC | scope_get_private_field | 4:var_name, 2:scope | . => . |
removed later in resolve_variables() |
|||
| BD | scope_get_private_field2 | 4:var_name, 2:scope | . => . |
removed later in resolve_variables() |
|||
| BE | scope_put_private_field | 4:var_name, 2:scope | . => . |
removed later in resolve_variables() |
|||
| BF | set_class_name | 4:class_offset | . => . |
| set class name | |||
| C0 | line_num | 4:line | . => . |
| debug line number | |||
Live Reload
kwui has a built-in live reload system. It allows you to change your JavaScript user interface source code and view the result in realtime.
Live Reload is currently only available for Windows Debug builds.
Usage
-
Load resource from local directory
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { let app = Application::new(); if cfg!(all(target_os = "windows", debug_assertions)) { app.set_resource_root_dir("{your assets dir}"); } }Then asset URLs like
:/entry.jswill be mapped to{your assets dir}/entry.js. -
While the application is running, pressing
F5to trigger Live Reload of current Dialog, the user interface will be re-built.Rust-side states are preserved, JavaScript module-level and component-level variables and states are re-initialized during reload.
How it works
- Increase application's script version.
- Reload entry module script
importwill also import a new version of dependent JavaScript modules.
- Call
builder()to build a new root component tree.- Child components in other JavaScript modules are built recursively.
- Patch old user interface with new root component tree.
- Garbage Collection will recycle old JavaScript module states later.